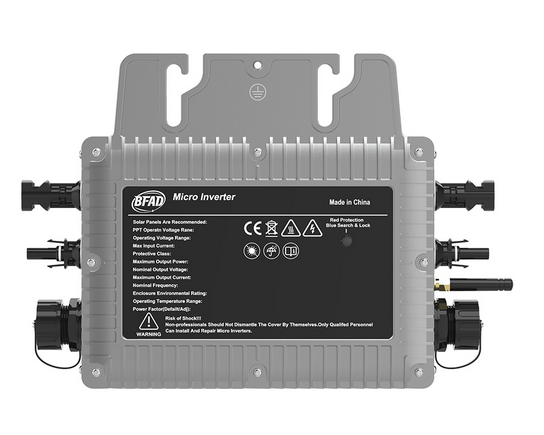
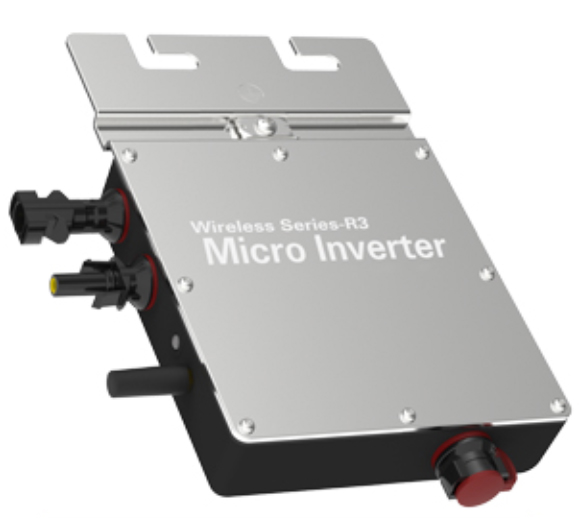
Series inverters and parallel inverters are a kind of inverters, they are different in the connection mode of inverters, with their own characteristics and application scenarios. The following will be compared from the working principle, advantages and disadvantages and application fields to further understand the difference between series inverters and parallel inverters.
First of all, the working principle of the series inverter is to connect multiple inverters in series together, the voltage output is equal to the sum of the output voltage of each inverter, and the current output is equal to the sum of the output current of each inverter. This series connection method can improve the output voltage and power, and is suitable for high voltage requirements. However, the series inverter will affect the stability of the whole system when the load is uneven or faulty.
The parallel inverter is to connect multiple inverters in parallel, the current output is equal to the sum of the output current of each inverter, and the voltage output is equal to the sum of the output voltage of each inverter. This parallel connection method can improve the output current and power, and is suitable for occasions with high current requirements. The advantage of parallel inverter is that it has good load balance, and the fault only affects a single inverter, and does not affect the operation of the whole system.
From the point of view of advantages and disadvantages, the advantage of series inverter is that it can improve the output voltage and power, suitable for high voltage requirements of the system, but the stability is relatively poor; The advantage of shunt inverters is that they have good load balancing and fault tolerance, and are suitable for systems with high current requirements, but they cannot increase the output voltage.
In the field of application, series inverters are usually used in systems that require high voltage output, such as HVDC transmission systems and HVDC power supply systems. Parallel inverters are usually used in systems that require high current output, such as electric vehicle charging systems and high-power inverter systems in industrial production.
In general, series inverters and parallel inverters have obvious differences in connection mode, working principle, advantages and disadvantages and application fields. According to the specific needs and system requirements, it is very important to choose the right inverter connection mode to ensure the operating stability and performance of the system to achieve the best state.


