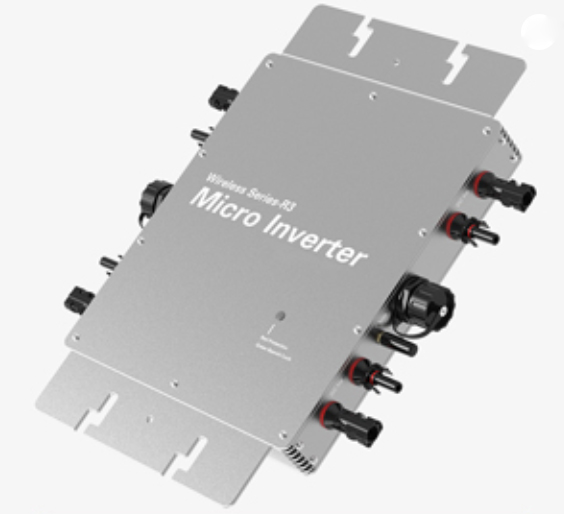
Photovoltaic inverter is the equipment that converts direct current into alternating current, and the inverter is one of the key components in the photovoltaic power generation system. The basic working principle of the photovoltaic inverter is as follows: When sunlight shines on the photovoltaic cell module, the photovoltaic cell module generates direct current, which is transmitted to the inverter through the bus or DC switch box. The inverter converts direct current into alternating current that can be fed directly to the grid.
Photovoltaic inverters accomplish this conversion process through several steps. First, the inverter uses a rectifier to convert direct current into alternating current. Then, the inverter uses PWM (pulse width modulation) technology or other technologies to modulate the alternating current to ensure that the output voltage and frequency of the alternating current meet the requirements of the grid. Finally, the inverter is filtered through a filter to ensure that the output AC is of good quality and does not interfere with the grid.
The working process of photovoltaic inverters is mainly affected by factors such as light intensity, battery module voltage and current. In order to improve the efficiency and stability of the inverter, modern photovoltaic inverters usually use maximum power point tracking technology (MPPT) and intelligent control algorithms to ensure that the inverter always works at the best working point and can adapt to work under different lighting conditions.
In general, the photovoltaic inverter plays a crucial role in the photovoltaic power generation system, which converts the direct current generated by the photovoltaic cell module into alternating current, and realizes the interconnection between the photovoltaic system and the power grid. By continuously improving the technical level and improving equipment performance, photovoltaic inverters will play a more important role in the future energy transition.